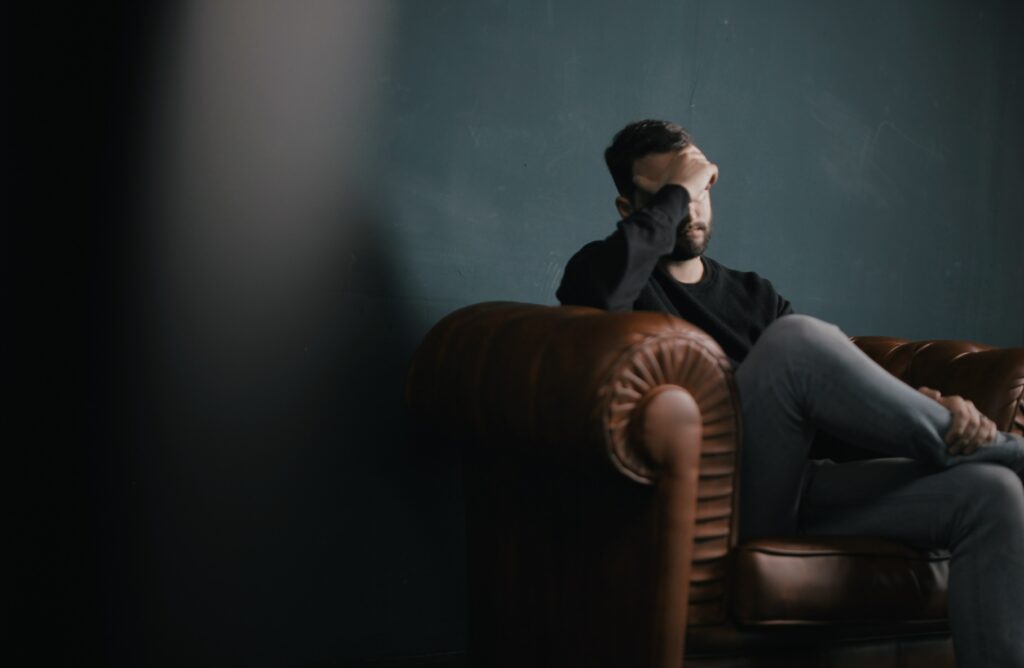
Many know that stress negatively affects mental health, but what happens to the body? Your physical health can be at risk if prolonged, intense stress is never addressed. Those with chronic stress may feel restless at night, have unexplainable sickness, and have trouble focusing on daily activities.
Physiological Impact of Chronic Stress on the Body
According to the American Psychological Association, chronic stress can increase the heart rate, which elevates stress hormones and blood pressure. Muscles may also be tense if never relaxed. This can cause body soreness and headaches. Stretching, exercising, and completing breathing exercises can help mitigate muscle tension, but chronic stress may need to be addressed by a mental health professional.
Chronic stress not only affects your mental well-being but can also lead to weight gain. Cortisol, a stress hormone, plays a crucial role in the body’s function, such as also overseeing how the body utilizes carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. When stress becomes excessive, cortisol production persists, resulting in weight gain, elevated blood sugar levels, digestive problems, and a weakened immune system.
How to Help Chronic Stress
Chronic stress may need several interventions to help. It is important to first identify the specific stressors to develop strategies to manage them. You can also read more about stress here.
Here are some ways to help manage chronic stress:
- Professional Help: If chronic stress persists or becomes overwhelming, consider seeking help from a mental health professional. Therapy, counseling, or other interventions may be beneficial in addressing underlying issues.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Make sure your daily routine includes exercise, a well-balanced diet, and sufficient sleep.
- Time Management: Prioritize tasks, set realistic goals, and break them down into manageable steps. Avoid overcommitting and learn to say no when necessary.
- Mindfulness Techniques: Incorporate mindfulness practices, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation into your daily routine.
- Social Connections: Cultivate and maintain supportive relationships. Sharing thoughts and feelings with friends, family, or a support network can provide emotional support during challenging times.
- Hobbies and Leisure Activities: Engage in activities you enjoy. Hobbies and leisure pursuits serve as healthy outlets for stress, providing a break from routine and promoting a sense of fulfillment.
- Physical Exercise: Regular physical activity is a natural stress reliever. Choose activities you enjoy, whether it’s walking, jogging, yoga, or other forms of exercise.
- Limit Stimulants: Reduce the consumption of stimulants like caffeine and nicotine, as they can contribute to increased anxiety and stress.
Managing chronic stress is a personal journey, so some strategies may not work for everyone. Consider seeking professional guidance to develop a personalized approach tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
Psychologists are ready to help! Create a form request here to begin your mental health journey.